 Database Structures
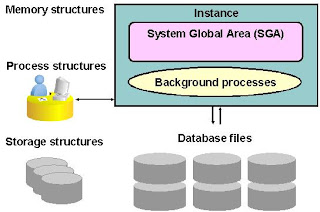
Database StructuresEach running Oracle database is associated with an Oracle instance. When a database is started on a database server, the Oracle software allocates a shared memory area called the System Global Area (SGA) and starts several Oracle background processes. This combination of the SGA and the Oracle processes is called an Oracle instance.
After starting an instance, the Oracle software associates the instance with a specific database. This is called mounting the database. The database is then ready to be opened, which makes it accessible to authorized users. Multiple instances can execute concurrently on the same computer, each accessing its own physical database.
You can look at the Oracle database architecture as various interrelated structural components.
An Oracle database uses memory structures and processes to manage and access the database. All memory structures exist in the main memory of the computers that constitute the database server. Processes are jobs that work in the memory of these computers. A process is defined as a “thread of control” or a mechanism in an operating system that can run a series of steps.
After starting an instance, the Oracle software associates the instance with a specific database. This is called mounting the database. The database is then ready to be opened, which makes it accessible to authorized users. Multiple instances can execute concurrently on the same computer, each accessing its own physical database.
You can look at the Oracle database architecture as various interrelated structural components.
An Oracle database uses memory structures and processes to manage and access the database. All memory structures exist in the main memory of the computers that constitute the database server. Processes are jobs that work in the memory of these computers. A process is defined as a “thread of control” or a mechanism in an operating system that can run a series of steps.
